728x90
스프링 시큐리티 아키텍쳐
스프링 시큐리티 아키텍쳐가 복잡하고 쉽지 않다.
부분별로 살펴보고 전체 그림을 맞춰본다 - (Divide and Conquer)
SecurityContextHolder와 Authentication
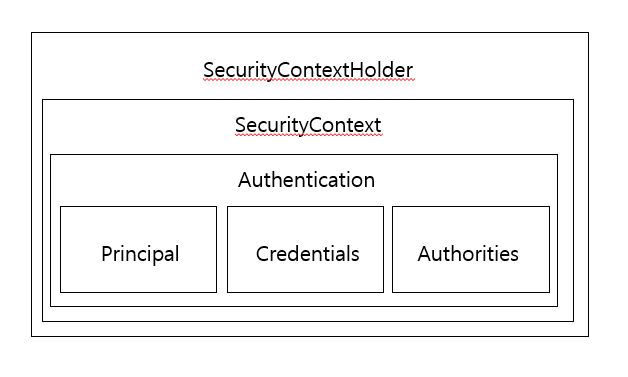
위와 같이 Authentication객체 안에서 principal를 담고 SecurityContext으로 감싸고 한번 더 SecurityContextHolder로 감싼 구조이다.
- SecurityContextHolder : Authentication를 SecurityContext로 담고 있는 객체
- SecurityContext : Authentication을 담고 있는 객체
- Authentication : principal, authorities, credentials을 담고 있는 객체
- principal : 사용자 정보(애플리케이션에서 인증을 거치고 난 인증정보)
- authorities : 사용자 권한
- credentials : SecurityContext를 제공하는 방법은 ThreadLocal을 사용 -> 파라미터를 넘기지 않아도 사용 가능
- ThreadLocal : 한 쓰레드 내에서 어디서나 접근 가능한 저장소
예시 코드
1. 소스 코드 살펴보기
@Controller
public class SampleController {
@Autowired SampleService sampleService;
@GetMapping("/dashboard")
public String dashboard(Model model, Principal principal){
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello " + principal.getName());
sampleService.dashboard();
return "dashboard";
}
}@Service
public class SampleService {
public void dashboard() {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
Object credentials = authentication.getCredentials();
boolean authenticated = authentication.isAuthenticated();
}
}- SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() : SecurityContextHolder에서 authentication을 반환 받는다.
- authentication.getPrincipal() : principal을 반환받는다. Object로 사실상 UserDetails 타입
- authentication.getAuthorities() : 사용자의 권한들을 반환. 이때 복수형인 이유는 여러개의 권한을 가질 수 있기 때문(유저이면서 동시에 관리자인 경우)
- authentication.getCredentials() : 인증한 다음에는 가지고 있을 필요가 없어서 null 값이 반환된다.
- authentication.isAuthenticated() : 사용자의 인증 여부를 boolean 타입으로 반환해준다.
2. 디버깅으로 살펴보기
authentication.getPrincipal()

- 폼 인증 같은 경우에는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 반환
-> Authentication 타입의 구현체인 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 객체가 SecurityContextHolder안에 Authentication으로 담기는 것이다. - authentication의 principal(User) = UserDetailsService에서 반환한 User
authentication.getAuthorities()
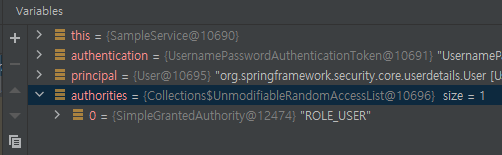
- SimpleGrantedAuthority를 생성할때(User빌드할때) .roles가 "ROLE_"를 추가해줌
(Authentication객체 안에 GrantAuthorities 도 꺼낼 수 있다)
authentication.getCredentials()
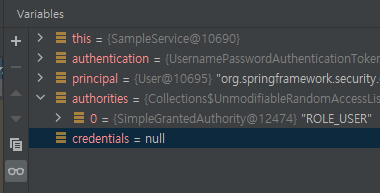
- credentials 값이 null인 것을 확인할 수 있다.
authentication.isAuthenticated()
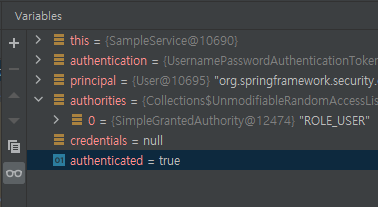
- 폼 인증의 경우 로그아웃 전까지는 true 반환
- OAuth와 같은 토큰을 사용하는 경우 토큰이 만료되면 false 반환
정리
- 인증을 거쳐서 들어왔기 때문에 SecurityContextHolder안에는 반드시 인증이 된 정보가 들어가게 되어있다.
- 인증이 되면 Authentication객체가 만들어지고 Authentication객체를 ContextHolder에 넣어줌
- ThreadLocal이 기본 전략이고 아래와 같은 전략들이 존재
- MODE_THREADLOCAL
- MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
- MODE_GLOBAL
- 우리가 어싱크 구현이 아닌 한 동일한 스레드가 그 요청을 처리하게 된다. (servlet thread per request)
- 서블릿 컨테이너(Tomcat)가 받아서 어떤 쓰레드에 어떻게 배정하는지는 Tomcat이 가지고 있는 앞단의 커넥터가 처리하는거고 애플레키이션에 들어와 요청을 처리하는거는 대부분 한 쓰레드가 처리한다.
- principal 정보를 넘겨주지 않더라도 임의대로 SecurityContext를 통해서 참조할 수 있다.
- UserDetailsService가 인증을 하는건 아니고 어디에 있든 유저 정보를 시큐리티한테 제공하는 역할을 한다.
- 인증을 하는 역할은 AuthenticationManager 한다.
참고 문서 : 인프런 Spring Security 강의
감사합니다.
728x90
'개발 > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MongoDB] MongoInterruptedException 해결하기 (0) | 2024.06.02 |
|---|---|
| RecoverableDataAccessException 해결한 경험 (1) | 2024.04.28 |
| Spring boot에 Swagger 적용하기 (0) | 2023.03.31 |
| Spring security + JWT 구현 방식 (0) | 2023.03.29 |
| Interceptor, DispatcherServlet이란? (0) | 2021.07.16 |




댓글